Javafx布局
JavaFX布局
(一)FlowPane面板
按照从上到下、从左到右的次序摆放,面板大小变化,会重新摆放各个控件的位置
首先创建一个FlowPane对象,代码如下:
FlowPane pane = new FlowPane();
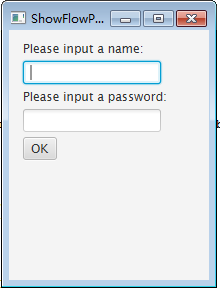
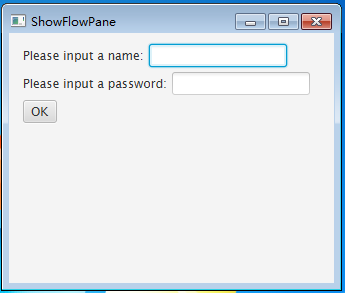
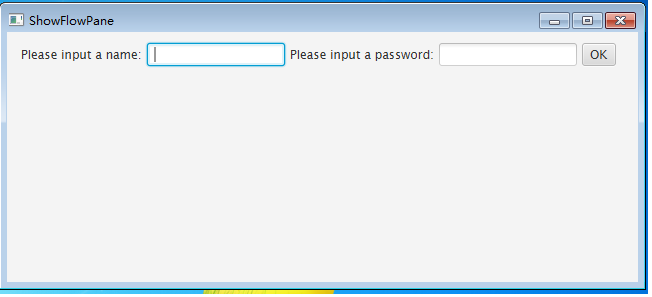
pane.setPadding(new Insets(11, 12, 13, 14)); pane.setHgap(5);//设置控件之间的垂直间隔距离 pane.setVgap(5);//设置控件之间的水平间隔距离创建两个标签对象、两个文本输入框和一个按钮对象,代码如下:
Label lbName = new Label(“Please input a name:”);
TextField tfName = new TextField(); Label lbPassword = new Label("Please input a password:"); TextField tfPassword = new TextField(); Button okbtn = new Button("OK");将这几个控件添加到面板中,代码如下:
pane.getChildren().addAll(lbName,tfName,lbPassword,tfPassword,okbtn);
当面板大小发生变化时
(二) GridPane面板
将整个面板划分为若干个格子,每个格子的大小是一样的,每个格子中可以放置一个控件
如下代码创建了一个GridPane对象:
GridPane pane = new GridPane();
pane.setAlignment(Pos.CENTER); pane.setPadding(new Insets(11.5, 12.5, 13.5, 14.5)); pane.setHgap(5.5); pane.setVgap(5.5);向面板中添加六个按钮,代码如下:
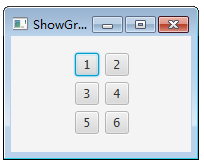
pane.add(new Button(“1”), 0, 0);
pane.add(new Button("2"), 1, 0); pane.add(new Button("3"), 0, 1); pane.add(new Button("4"), 1, 1); pane.add(new Button("5"), 0, 2); pane.add(new Button("6"), 1, 2);add方法的第二个和第三个参数是指定控件摆放的位置,分别表示所在的列和行,0是第一行和第一列。布局效果如下图所示:
(三) BorderPane面板
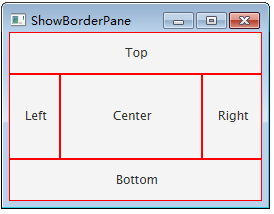
将整个面板划分五个区域,分别是上、下、左、右、中,每个区域可以放置一个控件。
首先创建一个BorderPane对象,代码如下:
BorderPane pane = new BorderPane();
然后在BorderPane对象的五个区域分别放置五个CustomPane对象,CustomPane是自定义面板,是为了方便放置标签。代码如下:
pane.setTop(new CustomPane(“Top”)); //放置在上面
pane.setRight(new CustomPane("Right"));//放置在右边 pane.setBottom(new CustomPane("Bottom"));//放置在上面 pane.setLeft(new CustomPane("Left"));//放置在左边 pane.setCenter(new CustomPane("Center"));//放置在中间
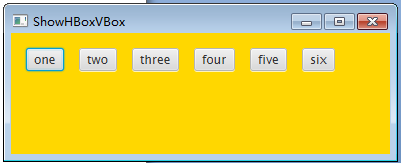
(四) HBox面板
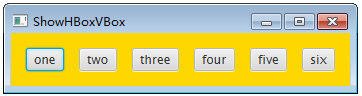
无论有多少个控件都是放在同一行
首先创建一个HBox对象,代码如下:
HBox hBox = new HBox(15);
hBox.setPadding(new Insets(15, 15, 15, 15)); hBox.setStyle("-fx-background-color: gold");然后,在面板上添加六个按钮,代码如下:
hBox.getChildren().add(new Button(“one”));
hBox.getChildren().add(new Button("two")); hBox.getChildren().add(new Button("three")); hBox.getChildren().add(new Button("four")); hBox.getChildren().add(new Button("five")); hBox.getChildren().add(new Button("six"));
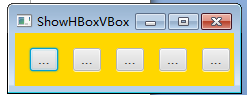
当面板大小发生变化时
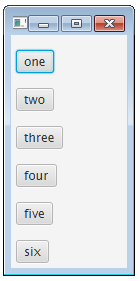
(五) VBox面板
将所有的控件放在同一列
首先创建一个VBox对象,代码如下:
VBox vBox = new VBox(15);
vBox.setPadding(new Insets(15, 5, 5, 5));然后,在VBox对象中添加六个按钮,代码如下:
vBox.getChildren().add(new Button(“one”));
vBox.getChildren().add(new Button("two")); vBox.getChildren().add(new Button("three")); vBox.getChildren().add(new Button("four")); vBox.getChildren().add(new Button("five")); vBox.getChildren().add(new Button("six"));
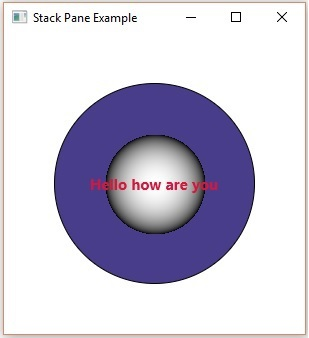
(六)StackPane
每个元素叠加在另一个元素上面
import javafx.application.Application; import javafx.collections.ObservableList; import javafx.geometry.Insets; import javafx.scene.Scene; import javafx.scene.layout.StackPane; import javafx.scene.paint.Color; import javafx.scene.shape.Circle; import javafx.scene.shape.Sphere; import javafx.scene.text.Font; import javafx.scene.text.FontWeight; import javafx.scene.text.Text; import javafx.stage.Stage; public class StackPaneExample extends Application { @Override public void start(Stage stage) { //Drawing a Circle Circle circle = new Circle(300, 135, 100); circle.setFill(Color.DARKSLATEBLUE); circle.setStroke(Color.BLACK); //Drawing Sphere Sphere sphere = new Sphere(50); //Creating a text Text text = new Text("Hello how are you"); //Setting the font of the text text.setFont(Font.font(null, FontWeight.BOLD, 15)); //Setting the color of the text text.setFill(Color.CRIMSON); //setting the position of the text text.setX(20); text.setY(50); //Creating a Stackpane StackPane stackPane = new StackPane(); //Setting the margin for the circle stackPane.setMargin(circle, new Insets(50, 50, 50, 50)); //Retrieving the observable list of the Stack Pane ObservableList list = stackPane.getChildren(); //Adding all the nodes to the pane list.addAll(circle, sphere, text); //Creating a scene object Scene scene = new Scene(stackPane); //Setting title to the Stage stage.setTitle("Stack Pane Example"); //Adding scene to the stage stage.setScene(scene); //Displaying the contents of the stage stage.show(); } public static void main(String args[]){ launch(args); } }
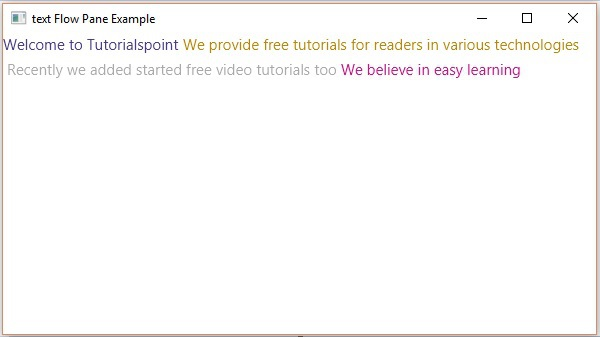
(七)Textflow
多个文本节点的流式布局
import javafx.application.Application; import javafx.collections.ObservableList; import javafx.scene.Scene; import javafx.scene.paint.Color; import javafx.scene.text.Font; import javafx.scene.text.Text; import javafx.scene.text.TextAlignment; import javafx.scene.text.TextFlow; import javafx.stage.Stage; public class TextFlowExample extends Application { @Override public void start(Stage stage) { //Creating text objects Text text1 = new Text("Welcome to Tutorialspoint "); //Setting font to the text text1.setFont(new Font(15)); //Setting color to the text text1.setFill(Color.DARKSLATEBLUE); Text text2 = new Text("We provide free tutorials for readers in various technologies "); //Setting font to the text text2.setFont(new Font(15)); //Setting color to the text text2.setFill(Color.DARKGOLDENROD); Text text3 = new Text("\n Recently we started free video tutorials too "); //Setting font to the text text3.setFont(new Font(15)); //Setting color to the text text3.setFill(Color.DARKGRAY); Text text4 = new Text("We believe in easy learning"); //Setting font to the text text4.setFont(new Font(15)); text4.setFill(Color.MEDIUMVIOLETRED); //Creating the text flow plane TextFlow textFlowPane = new TextFlow(); //Setting the line spacing between the text objects textFlowPane.setTextAlignment(TextAlignment.JUSTIFY); //Setting the width textFlowPane.setPrefSize(600, 300); //Setting the line spacing textFlowPane.setLineSpacing(5.0); //Retrieving the observable list of the TextFlow Pane ObservableList list = textFlowPane.getChildren(); //Adding cylinder to the pane list.addAll(text1, text2, text3, text4); //Creating a scene object Scene scene = new Scene(textFlowPane); //Setting title to the Stage stage.setTitle("text Flow Pane Example"); //Adding scene to the stage stage.setScene(scene); //Displaying the contents of the stage stage.show(); } public static void main(String args[]){ launch(args); } }
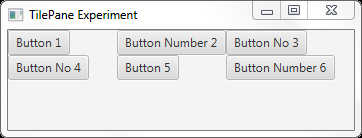
(八)TilePane
TilePane是一个类似于FlowPane的容器。 但是它与FlowPane不同,因为子组件列在相同大小的单元格上。
package com.jenkov.javafx.layouts; import javafx.application.Application; import javafx.geometry.Pos; import javafx.scene.Scene; import javafx.scene.control.Button; import javafx.scene.layout.TilePane; import javafx.stage.Stage; public class TilePaneExperiments extends Application { @Override public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception { primaryStage.setTitle("TilePane Experiment"); Button button1 = new Button("Button 1"); Button button2 = new Button("Button Number 2"); Button button3 = new Button("Button No 3"); Button button4 = new Button("Button No 4"); Button button5 = new Button("Button 5"); Button button6 = new Button("Button Number 6"); TilePane tilePane = new TilePane(); tilePane.getChildren().add(button1); tilePane.getChildren().add(button2); tilePane.getChildren().add(button3); tilePane.getChildren().add(button4); tilePane.getChildren().add(button5); tilePane.getChildren().add(button6); tilePane.setTileAlignment(Pos.TOP_LEFT); Scene scene = new Scene(tilePane, 200, 100); primaryStage.setScene(scene); primaryStage.show(); } public static void main(String[] args) { Application.launch(args); } }